Botox Tips for Dentists Administering Botox for TMJ Muscle Pain
1. Take a comprehensive course before administering Botox to patients.
2. Perform Muscle Examination before administering Botox to identify the affected muscles.
3. Use a tissue marker during palpation to identify pain points.
4. Have an assistant record patient responses to muscle examination during the muscle examination.
5. Perform preliminary Anesthetic challenges to assess whether muscle respond (VAS Scale)
5. Keep Ethyl Chloride on hand to relieve immediate jaw tension.
6. Consider using a laser to relieve immediate muscle and headache pain for patients who have TMJ Muscle Myalgia.
7. Perform injections bilaterally to maintain the relative strength of bilateral muscles.
8. Add Lidocaine to Botox injections for immediate pain relief.
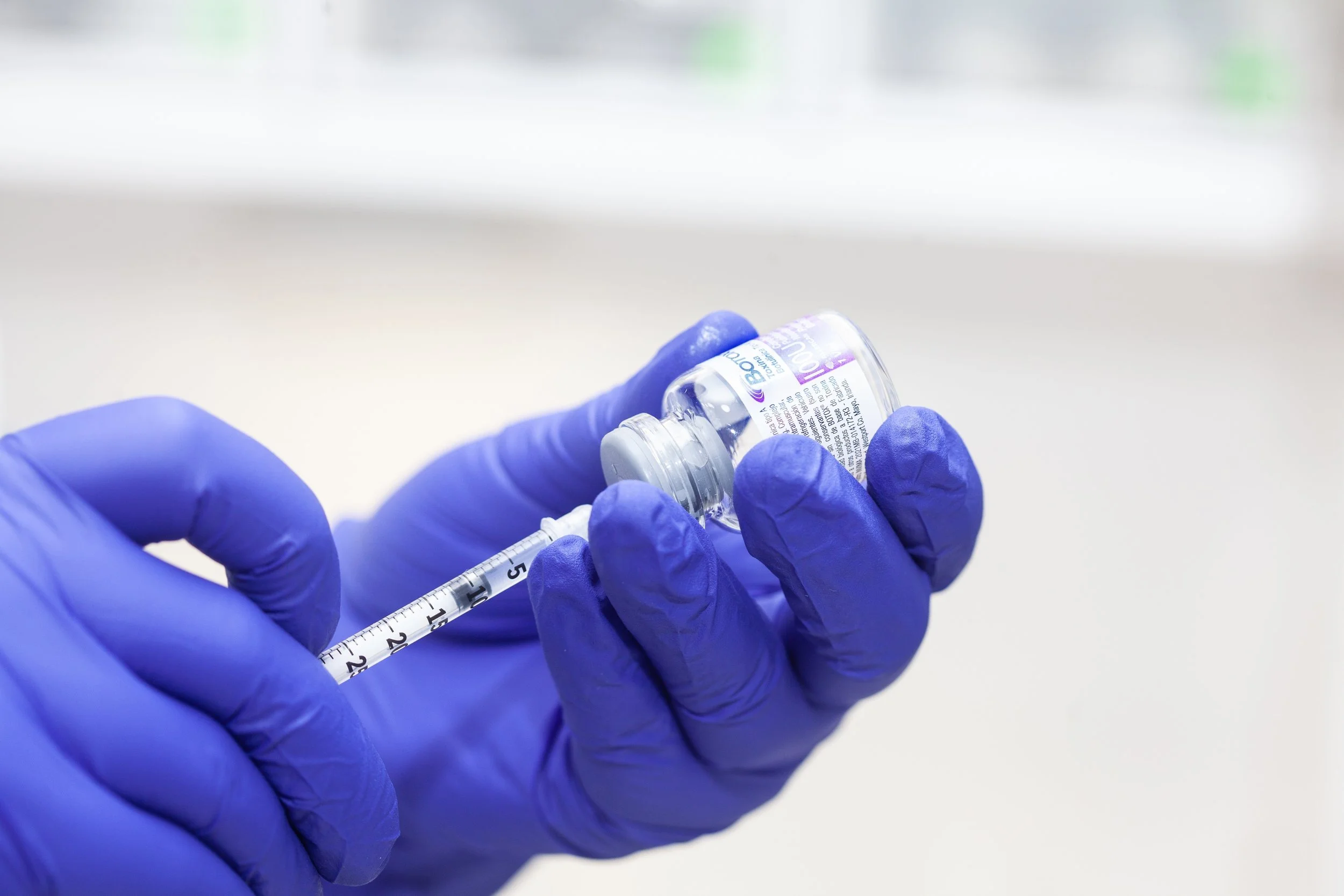
9. Draw a volume of air into the Botox syringe prior to drawing the Botox. Express the air into the Botox vial (not into the liquid Botox solution so as not to create air bubbles), draw the Botox solution into the vial.
10. Do not shake the Botox vial during reconstitution. Use gentle wrist motion to incorporate the powder into the liquid saline.
11. Use Lidocaine to reconstitute Botox of 0.9% Sterile Saline is not available. Do not use Lidocaine Carpules, use Lidocaine without epinephrine drawn from a vial.
12. When injecting the temporalis muscle, do not touch bone. Insert the 8 mm needle halfway into the muscle.
13. Trigger point injections can be use in conjunction with Botox injections
14. When injecting the Orbicularis Oculi, inject Botox away from the eye while palpating the orbit of the eye.
15. When Injecting, grasp the muscle while injecting Botox.